Recently, the internationally renowned journal Toxicological Sciences published the latest research paper of heavy metal cadmium induced immunotoxicity by Professor Shi Haifeng's group of Jiangsu University. The paper is entitled "Inhibition of Autophagy Alleviates Cadmium-Induced Mouse Spleen and Human B Cells Apoptosis". This study has theoretical significance and application value for further enriching the molecular mechanism and preventing cadmium and other heavy metals induced immunotoxicity.

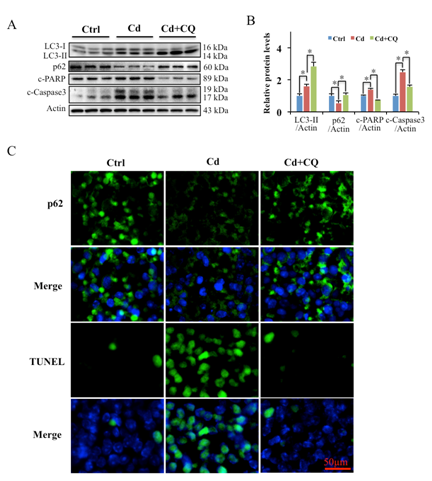
Cadmium (Cd) is a toxic heavy metal that can accumulate and cause severe damage to many organs, such as liver, kidney, lung, etc. Cd also significantly suppresses immunity, however, the underlying mechanism involved in Cd-induced immunnotoxicity is still unclear. The present study indicated that semi-chronic Cd exposure (7 days) induced apoptotic damage of mouse spleen. In human Ramos B cells, Cd exposure also induced apoptosis, which was dependent on Cd- induced vacuole membrane protein 1 (VMP1) expression and autophagy. Cd-induced autophagy and apoptosis were abated when VMP1 expression was knockdown. In addition, Cd-induced VMP1 expression, autophagy, and apoptosis were dependent on the elevation of Ca2+ and reactive oxygen species (ROS). More important, Cd exposure also induced VMP1 expression and autophagy in mouse spleen tissue, and the intraperitoneal injection of the autophagy inhibitor chloroquine (CQ) into mice effectively reduced Cd-induced spleen apoptotic damage. Taken together, these results indicate Cd-induced autophagy, promotes apoptosis in immune cells, and inhibition of autophagy can alleviate Cd-induced spleen and immune cell apoptosis. This study might provide the groundwork for future studies on Cd-induced immunomodulatory effects and immune diseases.
Professor Shi Haifeng of Jiangsu University is the corresponding author of the paper. Associate Professor Gu Jie of Jiangsu University, postgraduate students Wang Yanwei, Liu Yanmin and Shi Meilin are co-first authors of the thesis, Yin Liangdong, Third Affiliated Hospital of Jiangsu University, Professor Chris Kong Chu Wong, Department of Biology, Hong Kong Baptist University, and Professor Guo Zhigang, Jiangsu Key Laboratory for Molecular and Medical Biotechnology, College of Life Science, Nanjing Normal University Participated in this research work. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China.
Original link: https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfz089
Gu Jie reports